|
General information:
 Gram-negative coccobacilli. Gram-negative coccobacilli.
 The name of the genus Haemophilus (meaning blood loving) refers to the dependence of the organism on heme-related molecules for growth under aerobic conditions. The name of the genus Haemophilus (meaning blood loving) refers to the dependence of the organism on heme-related molecules for growth under aerobic conditions.
Characteristics:
 H. influenzae, an obligate human commensal found principally in the upper respiratory tract,meet the requirements of its relatively simple filestyle with a small genome that lacks many regulatory circuits. H. influenzae, an obligate human commensal found principally in the upper respiratory tract,meet the requirements of its relatively simple filestyle with a small genome that lacks many regulatory circuits.
 H. influenzae is capable fo generating distinct phenotypes that differ primarily in expression of surface proteins and LPS components due to microsatellites, which are rare in the Enterobactereacae but are common among other Gram-negative mucosal pathogens such as Neisseria and Helicobacter. H. influenzae is capable fo generating distinct phenotypes that differ primarily in expression of surface proteins and LPS components due to microsatellites, which are rare in the Enterobactereacae but are common among other Gram-negative mucosal pathogens such as Neisseria and Helicobacter.
Disease:
 Systemic infections such as bacteraemia, meningitis, septic arthritis and pneumonia in young children are caused primarily by H. influenzae possessing the type b capsule (Hib). Systemic infections such as bacteraemia, meningitis, septic arthritis and pneumonia in young children are caused primarily by H. influenzae possessing the type b capsule (Hib).
 Respiratory infections such as pneumonia, otitis media, sinusitis, and bronchitis are caused primarily by non-encapsulated strains. Respiratory infections such as pneumonia, otitis media, sinusitis, and bronchitis are caused primarily by non-encapsulated strains.
Selected genomes: ⇒ comparative pathogenomics ⇐
 H. ducreyi 35000HP, 1698955 bp, NC_002940 H. ducreyi 35000HP, 1698955 bp, NC_002940
 H. influenzae 86-028NP, 1914490 bp, NC_007146 H. influenzae 86-028NP, 1914490 bp, NC_007146
 H. influenzae F3031, 1985832 bp, NC_014920 H. influenzae F3031, 1985832 bp, NC_014920
 H. influenzae PittEE, 1813033 bp, NC_009566 H. influenzae PittEE, 1813033 bp, NC_009566
 H. influenzae PittGG, 1887192 bp, NC_009567 H. influenzae PittGG, 1887192 bp, NC_009567
 H. influenzae R2866, 1932306 bp, CP002277 H. influenzae R2866, 1932306 bp, CP002277
 H. influenzae Rd KW20, 1830138 bp, NC_000907 H. influenzae Rd KW20, 1830138 bp, NC_000907
 H. somnus 129PT, 2007700 bp, NC_008309 H. somnus 129PT, 2007700 bp, NC_008309
 H. somnus 2336, 2263857 bp, NC_010519 H. somnus 2336, 2263857 bp, NC_010519
Genome-related publications:
 Fleischmann RD, et al., 1995. Whole-genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Science 269(5223):496-512. Fleischmann RD, et al., 1995. Whole-genome random sequencing and assembly of Haemophilus influenzae Rd. Science 269(5223):496-512.
 Harrison A, et al., 2005. Genomic sequence of an otitis media isolate of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae: comparative study with H. influenzae serotype d, strain KW20. J Bacteriol 187(13):4627-4636. Harrison A, et al., 2005. Genomic sequence of an otitis media isolate of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae: comparative study with H. influenzae serotype d, strain KW20. J Bacteriol 187(13):4627-4636.
 Challacombe JF, et al., 2007. Complete genome sequence of Haemophilus somnus (Histophilus somni) strain 129Pt and comparison to Haemophilus ducreyi 35000HP and Haemophilus influenzae Rd. J Bacteriol 189(5):1890-1898. Challacombe JF, et al., 2007. Complete genome sequence of Haemophilus somnus (Histophilus somni) strain 129Pt and comparison to Haemophilus ducreyi 35000HP and Haemophilus influenzae Rd. J Bacteriol 189(5):1890-1898.
 Hogg JS, et al., 2007. Characterization and modeling of the Haemophilus influenzae core and supragenomes based on the complete genomic sequences of Rd and 12 clinical nontypeable strains. Genome Biol 8(6):R103. Hogg JS, et al., 2007. Characterization and modeling of the Haemophilus influenzae core and supragenomes based on the complete genomic sequences of Rd and 12 clinical nontypeable strains. Genome Biol 8(6):R103.
Major virulence factors in Haemophilus:

 - H. ducreyi - H. ducreyi

















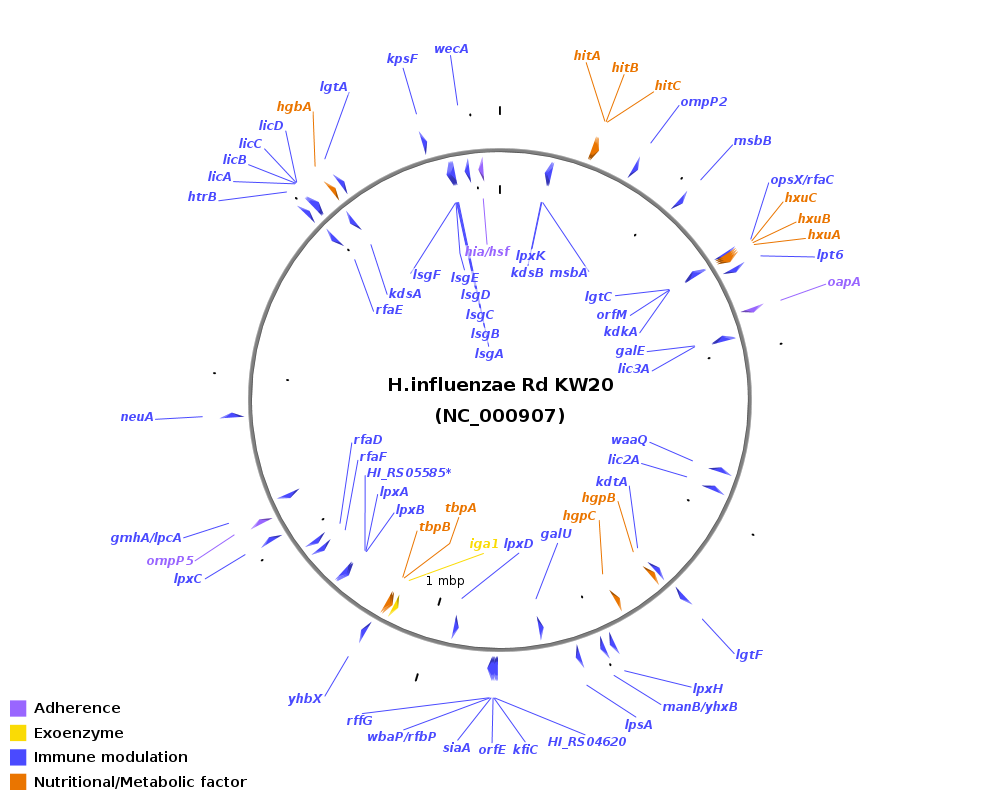
Genomic location of virulence-related genes in Haemophilus:
 |
Reported anti-virulence compounds to Haemophilus:






 |
| Back to Top |
|
